Picture this: a serene forest teeming with life, a bustling city park alive with activity, or even the seemingly mundane backyard. Every living thing in these environments is intricately connected, woven into a magnificent tapestry of relationships known as the food web. But understanding these connections can seem daunting, especially for students just beginning to explore the world of ecology. Enter the food web and food chain worksheet, a powerful tool to unravel the mysteries of life’s interconnectedness.
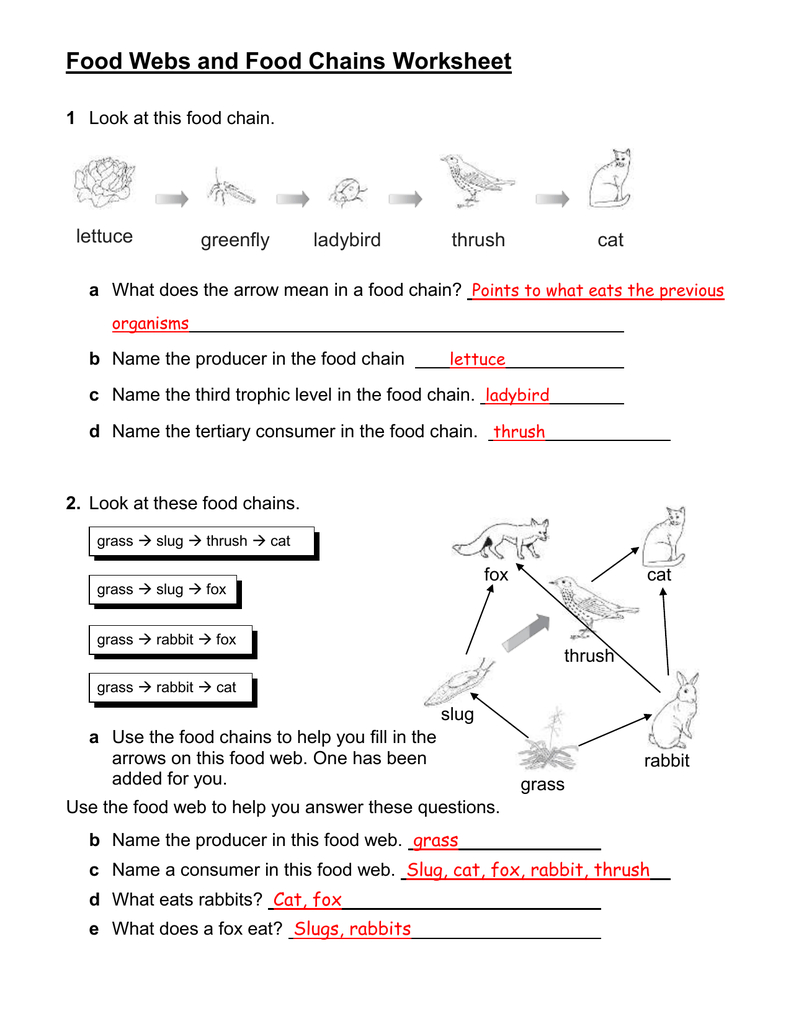
Image: davida.davivienda.com
These worksheets serve as valuable guides, providing a structured framework for learners to explore the fascinating world of predator-prey relationships, energy flow through ecosystems, and the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. Through hands-on activities, students gain a deeper understanding of how each organism plays a crucial role in the grand scheme of things, empowering them to appreciate the beauty and interconnected nature of our planet’s biodiversity.
Unveiling the Interplay of Life: Understanding the Food Chain
At the heart of the food web and food chain worksheet lies the concept of the food chain—a linear sequence that depicts the transfer of energy from one organism to another. Imagine a simple food chain consisting of a plant, a grasshopper, a frog, and a snake. The plant, a producer, harnesses energy from the sun through photosynthesis; the grasshopper, a primary consumer, feeds on the plant; the frog, a secondary consumer, consumes the grasshopper; and finally, the snake, a tertiary consumer, devours the frog. This chain illustrates the flow of energy, starting with the sun and moving through each organism.
Exploring the Delicate Web: Unveiling the Food Web
While the food chain provides a simplified view of energy flow, the food web showcases the complex network of interactions within an ecosystem. Think of it as a tangled web, where multiple food chains intertwine. Consider our previous example; while the grasshopper primarily eats plants, it might also be consumed by a bird, adding another chain to the web. Furthermore, the frog might also feed on other insects besides grasshoppers, further complicating the network of relationships.
The Importance of the Food Web: Maintaining Ecological Balance
Food webs are crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. Every organism plays a role, and disruptions can have cascading effects. Imagine what happens if a disease decimates a significant portion of a predator species. The prey population might skyrocket, leading to overgrazing and habitat destruction. Conversely, if a prey species is severely depleted, its predators may struggle to find food, leading to population decline or even extinction.

Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Delving into the World of Food Web and Food Chain Worksheets
Food web and food chain worksheets offer a variety of engaging activities aimed at fostering understanding and appreciation for the intricate world of ecological relationships. These activities can include:
1. Building Food Webs:
Students can create their own food webs using visuals, cards, or even virtual tools. This hands-on activity allows them to understand the interconnectedness of organisms within an ecosystem.
2. Analyzing Food Chain Diagrams:
By examining pre-made food chain diagrams, students can identify producers, consumers, and decomposers, as well as the flow of energy and matter through different trophic levels.
3. Identifying Trophic Levels:
Students can be challenged to categorize organisms based on their position in the food chain, understanding the concept of primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers.
4. Investigating Real-World Ecosystems:
Using case studies or local examples, students can explore real-life ecosystems and identify the food web interactions that sustain them. This can include studying the impact of human activity on different food webs.
5. Role-Playing Food Web Scenarios:
Students can act out the roles of different organisms in a simulated food web, gaining a deeper understanding of how interactions and changes can affect the ecosystem’s balance.
Applications of Food Web and Food Chain Knowledge
Understanding the intricate world of food webs and food chains is essential for addressing pressing environmental challenges. These concepts play a crucial role in:
1. Conservation Efforts:
By comprehending the interconnectedness of ecosystems, conservationists can develop strategies to protect endangered species, manage habitats, and mitigate the impacts of human activity.
2. Sustainable Agriculture:
Food web knowledge helps farmers to create healthy and balanced agricultural ecosystems, minimizing reliance on pesticides and promoting biodiversity.
3. Fisheries Management:
By understanding the food web dynamics in marine environments, scientists can make informed decisions about fishing quotas and manage fish populations sustainably.
4. Disease Control:
Understanding how disease outbreaks spread through food webs can help public health officials take preventive measures and control the spread of pathogens.
Food Web And Food Chain Worksheet
Embracing the Interconnected Nature of Life: A Final Note
As we navigate through a world facing numerous ecological challenges, understanding the interconnectedness of life becomes increasingly vital. Food web and food chain worksheets serve as valuable tools, empowering learners to explore this fascinating world, fostering appreciation for the delicate balance of nature, and ultimately, inspiring them to become responsible stewards of our planet.





