Ever found yourself staring at a blinking dashboard light, feeling a surge of apprehension as you wonder what the culprit could be? Or perhaps you’re ready to tackle a DIY project and need to know exactly where to find that elusive fuse. Knowing your way around the 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse box diagram is a vital skill for any owner, offering a window into the vehicle’s electrical system and empowering you to handle minor issues with confidence. This guide delves into the heart of your Transit Connect’s fuse box, providing you with the knowledge and tools to master the mysteries it holds.
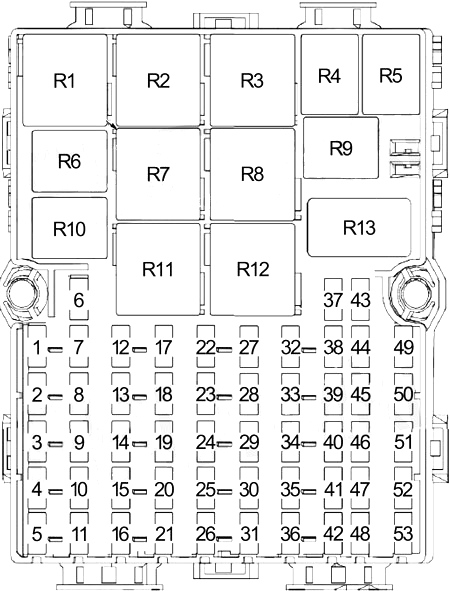
Image: mydiagram.online
The fuse box, often referred to as the “fuse panel,” serves as the command center for your vehicle’s electrical system. It houses an array of fuses, each safeguarding a specific circuit within the car. Fuses act as safety devices, preventing damage to your vehicle’s electrical components by interrupting the flow of electricity if an overload or short circuit occurs. Think of them as tiny heroes silently protecting your Transit Connect from electrical meltdowns!
Decoding the 2013 Ford Transit Connect Fuse Box Diagram
Navigating the 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse box diagram is like deciphering a map of your vehicle’s electrical network. Each fuse is assigned a specific location within the box, and its function is outlined in the diagram. It’s a practical guide, offering a quick reference for identifying and replacing a blown fuse. But what’s the best way to interpret this vital diagram?
Mastering the Basics
Before diving into the nuances of the diagram, let’s establish the fundamentals. The fuse box within the 2013 Ford Transit Connect typically boasts two compartments: the main fuse box and the under-hood fuse box. The main fuse box is usually found inside the passenger compartment, often located beneath the dashboard or within the glove box. The under-hood fuse box, as the name implies, is situated within the engine bay. Both contain crucial fuses that safeguard different systems within the vehicle.
Reading the Language of the Diagram
The fuse diagram itself is a visual roadmap. Each fuse is typically represented by its amperage rating, the fuse’s function, and its position within the fuse box. A common example: “10A – Radio.” This means the fuse is rated at 10 amps and controls the radio circuitry. Some diagrams may also include the location of the fuse box, a color-coded key to identify fuse types, and additional information like relay locations. Don’t be afraid to consult your owner’s manual for a more detailed explanation of your specific fuse box diagram.
![[DIAGRAM] Ford Transit Fuse Box Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://fuse-box.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Ford-Transit-Connect-2010-2013_20180529121559868_10.jpg)
Image: mydiagram.online
Locating the Fuse Box
Finding your 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse boxes is a crucial first step. Here are a few pointers to help you identify their exact locations:
- Main Fuse Box: Start by checking under the dashboard, specifically on the driver’s side. If you have a glove box, it may be situated within that compartment.
- Under-Hood Fuse Box: Open your hood and look for a black or grey box typically near the battery. Sometimes it’s located on the driver’s side fender, behind the battery cover.
Understanding Fuse Types and Amperage
Fuse boxes are often filled with a variety of fuse types, each designed to handle specific electrical loads. Common types include:
- Blade Fuses: These have a rectangular shape with a metal strip separating two terminals. They are prevalent in modern vehicles due to their ease of replacement and adaptability to different amperage ratings.
- Mini Fuses: Smaller and thinner than blade fuses, they are typically used for lower-amperage circuits. They are often located in the accessory compartments of vehicles.
- ATO Fuses: These traditional fuses have a cylindrical glass body with a thin wire inside. They are less common in newer vehicles but can still be found in certain circuits.
Amperage: The Key to Electrical Protection
Every fuse has an amperage rating that signifies its ability to withstand a specific amount of electrical current. If the current flow exceeds the fuse’s rating, the fuse will melt, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the electrical system. This is why it’s crucial to use the correct amperage fuse when replacing a blown one. Using a fuse with a higher amperage will not protect your vehicle’s electrical components, putting them at risk of damage.
Troubleshooting and Replacing Fuses
Armed with your 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse box diagram, you’re ready to tackle those electrical gremlins! But before you start swapping fuses, remember to always disconnect the battery to prevent accidental shocks.
1. Identify the Fuses
Start by consulting the fuse box diagram to identify the fuses that control the affected system. If your radio is out, for instance, the diagram would guide you to the fuse that powers the audio system.
2. Check for Blown Fuses
Open the fuse box and locate the identified fuses. A blown fuse will usually have a broken wire inside the glass body, or the fuse will be melted or discolored. Inspect each fuse carefully for any signs of damage.
3. Replace the Blown Fuse
If you’ve found a blown fuse, it’s time to replace it. Always use the correct amperage fuse as specified in your fuse box diagram. Simply insert the new fuse into the empty slot, ensuring it’s properly seated. Don’t force it; if it’s not going in smoothly, double-check the fuse type and the slot.
Addressing Common Electrical Issues in the 2013 Ford Transit Connect
The 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse box diagram can be your guide in addressing a host of common electrical problems. Here’s a glimpse into some common issues that can be tackled with a little know-how:
1. Headlights Not Working
If your headlights are giving you trouble, consult the fuse box diagram for the “Headlights” or “Low Beam” fuse, and check it for damage. If it’s blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage.
2. Power Windows Malfunctioning
Are your power windows refusing to cooperate? The diagram will often indicate separate fuses for each window circuit. Check the corresponding fuse for damage and replace it if needed.
3. Radio Silence
A quiet radio can be a real disappointment! The fuse box diagram will reveal the fuse responsible for the radio and audio system. Inspect it for any signs of breaking or melting, and replace it if necessary.
4. Dashboard Lights Flickering
Dashlights that flicker or refuse to illuminate can be a sign of a faulty fuse or loose connection within the fuse box. Check the diagram for the fuse that powers the dashboard lights and inspect it for damage. If the fuse is fine, it may be worth inspecting the connections within the fuse box to ensure they are secure.
Additional Tips for Maintaining Your Fuse Box
Keeping your fuse box in top shape can prevent future electrical woes. Here are some useful tips to keep in mind:
- Regular Inspection: Take a moment to visually inspect your fuse box every few months. This will help you identify any potential issues such as corrosion, loose connections, or damaged fuses before they cause serious problems.
- Keep Your Wiring Tidy: Check for any frayed or chafed wiring connected to the fuse box. Damaged wiring can lead to short circuits, which can damage your vehicle’s electrical system. Replace any frayed or damaged wiring promptly.
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: Your owner’s manual often offers valuable information about fuse box maintenance, troubleshooting, and recommended replacement parts.
2013 Ford Transit Connect Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion
Mastering the 2013 Ford Transit Connect fuse box diagram grants you a valuable insight into your vehicle’s electrical system, empowering you to address minor electrical issues independently. With a little patience, attention to detail, and a dose of caution, you can confidently navigate the labyrinth of fuses and wires, ensuring your Transit Connect remains a reliable and enjoyable companion on the road. So, grab that fuse box diagram, embrace the challenge, and unlock the potential to become a true master of your vehicle’s electrical workings!





