Imagine this: You’ve been working hard, exceeding expectations, putting in extra hours to meet tight deadlines. But when payday rolls around, you realize your paycheck hasn’t reflected your dedication. The extra time you dedicated to your company has gone unnoticed. This isn’t just a fictional scenario, it’s a common experience for many who haven’t fully grasped the complexities of overtime pay regulations.
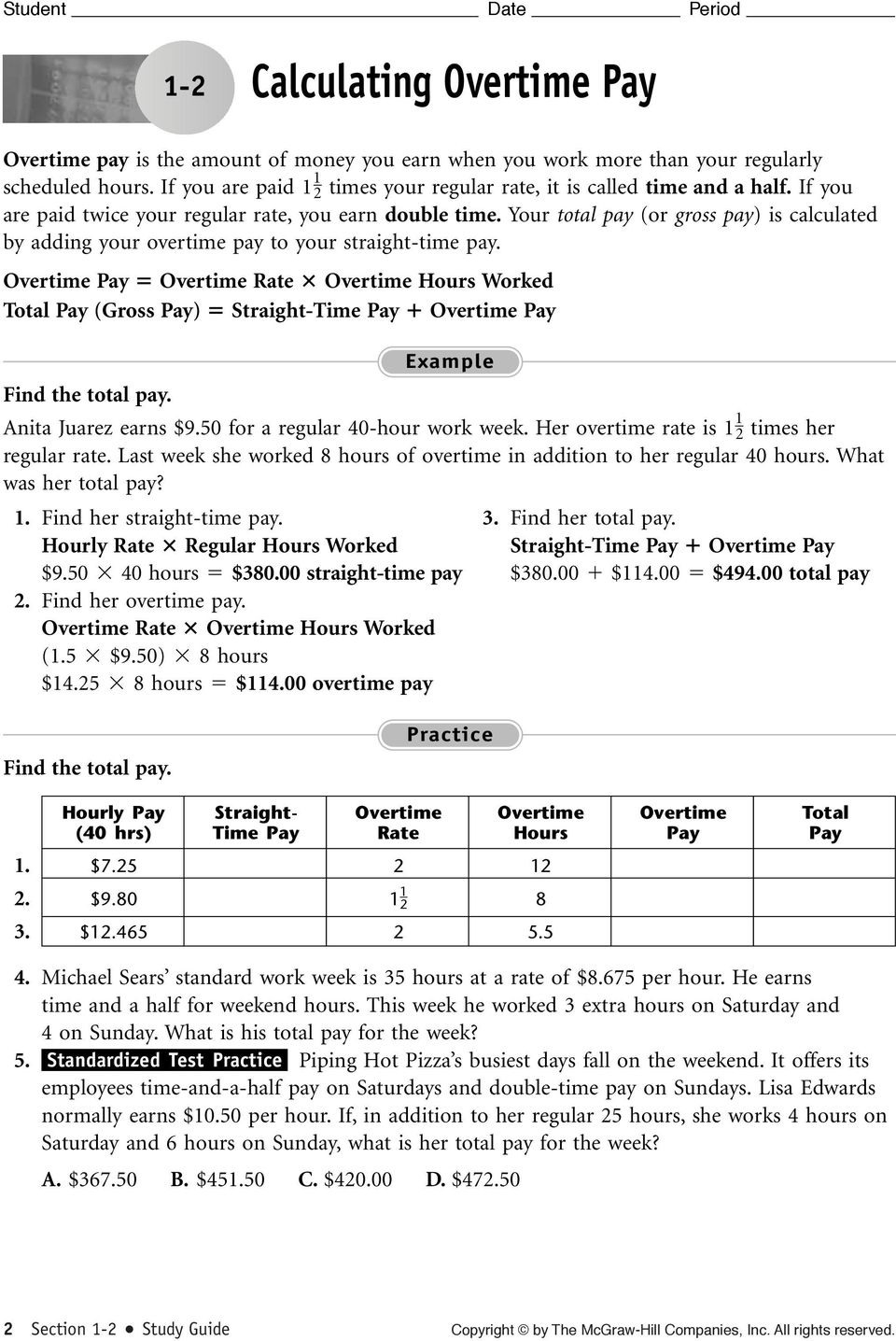
Image: quizzschoolreptilian.z13.web.core.windows.net
This article delves into the intricate world of overtime pay, guiding you through Lesson 1.2, a crucial aspect of workplace rights. We’ll explore the regulations, dissect the answer key and empower you with the knowledge to understand and advocate for your rightful compensation.
Diving Deep into Overtime Pay: Unveiling the Key to Fair Compensation
Overtime pay is a fundamental concept in labor law, ensuring workers receive additional compensation for hours worked exceeding a specific threshold. But this seemingly simple principle often sparks confusion. Lesson 1.2 aims to demystify this concept, breaking down the essential components to understand your legal entitlement.
Delving into the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
The backbone of overtime pay regulations lies in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Enacted in 1938, the FLSA aims to establish a fair minimum wage and protect workers from exploitative working conditions. This pivotal legislation mandates that employees who work more than 40 hours within a standard workweek are entitled to overtime pay, usually calculated at 1.5 times their regular hourly rate.
Uncovering the Fine Print: Exemptions and Exceptions
While the FLSA provides a solid foundation, it’s important to acknowledge that certain exceptions and exemptions exist. Understanding these nuances is critical to accurately interpreting your overtime pay rights. Let’s examine some key exemptions:
1. Executive, Administrative, and Professional Exemptions: These categories typically refer to employees who hold positions with substantial decision-making authority, management responsibilities, or specialized skills.
2. Computer Employees Exemption: This exemption applies to employees who work primarily on computer-related tasks, meeting specific criteria outlined in the FLSA.
3. Outside Sales Exemption: Employees who primarily work outside the office, selling goods or services, often fall under this exemption.
4. Seasonal or Recreational Employees: Employees working in seasonal or recreational industries sometimes qualify for exemptions, particularly if their employment period is short-term and predictable.

Image: www.pdffiller.com
Navigating the Maze: Overtime Pay Calculation
The FLSA spells out specific rules for calculating overtime pay. Let’s break it down:
- Regular Rate of Pay: This includes your base hourly rate, plus any non-discretionary bonuses, commissions, or shift differentials.
- Overtime Pay Calculation: Your overtime rate is calculated by multiplying your regular rate of pay by 1.5.
- Workweek: The FLSA defines the workweek as a fixed, recurring period of 168 hours, typically Sunday through Saturday.
Real World Examples: Bringing Lesson 1.2 to Life
Let’s illustrate how overtime pay works with practical examples:
Example 1: Imagine you work as a sales associate, earning $15 per hour. In one week, you work 50 hours. Your overtime pay calculation would be:
- Regular Hours: 40 hours * $15/hour = $600
- Overtime Hours: 10 hours $15/hour 1.5 = $225
- Total Earnings: $600 + $225 = $825
Example 2: Let’s say you are a graphic designer who meets the FLSA exemptions. You put in 55 hours a week, but since your work falls under the exemptions, you are not eligible for overtime pay.
Ensuring Fairness: Tracking Your Hours and Filing Complaints
Accurately tracking your hours worked is a crucial step in securing your overtime pay rights. Keep a detailed record of your work hours, including start and end times, any breaks, and any overtime hours. Many employers provide time tracking systems for employees to record their hours worked efficiently.
If you believe your employer is violating your overtime pay rights, you can take steps to address the situation.
- Communication: Initially, try communicating your concerns directly with your employer.
- Filing a Complaint: You can file a complaint with the Wage and Hour Division of the U.S. Department of Labor.
Expert Insights: Your Guide to Overtime Pay Navigations
When it comes to navigating the complexities of overtime pay, seeking expert guidance is always recommended. Consulting with an employment attorney specializing in labor law can provide you with personalized advice and legal support. They can help you understand your specific rights and obligations, decipher the intricacies of the FLSA, and navigate any conflicts with your employer.
Actionable Steps: Empowering You with Knowledge
Here are a few actionable steps you can take to protect your overtime pay rights:
- Familiarize Yourself with the FLSA: Understand the core provisions and exemptions outlined within the Fair Labor Standards Act.
- Stay Organized: Maintain accurate records of your work hours, diligently tracking all overtime hours.
- Communicate Openly: Maintain open communication with your employer regarding your work hours and compensation.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with an employment attorney for personalized guidance and legal support when needed.
Lesson 1.2 Overtime Pay Answer Key
Final Thoughts: Understanding Your Rights – A Foundation for Fairness
Understanding your overtime pay rights is a crucial step in ensuring fair compensation for your hard work. By familiarizing yourself with the nuances of Lesson 1.2, you empower yourself to advocate for your legal entitlements and build a fair and respectful work environment.
Remember, navigating the intricacies of labor law can be challenging. Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice for personalized guidance and legal support. Your time and dedication deserve to be recognized and fairly compensated.





