Have you ever wondered why the price of gasoline fluctuates so wildly or why the cost of a new iPhone seems to stay stubbornly high? These everyday economic phenomena are all governed by the intricate relationship between supply and demand, the invisible hand that guides the market.
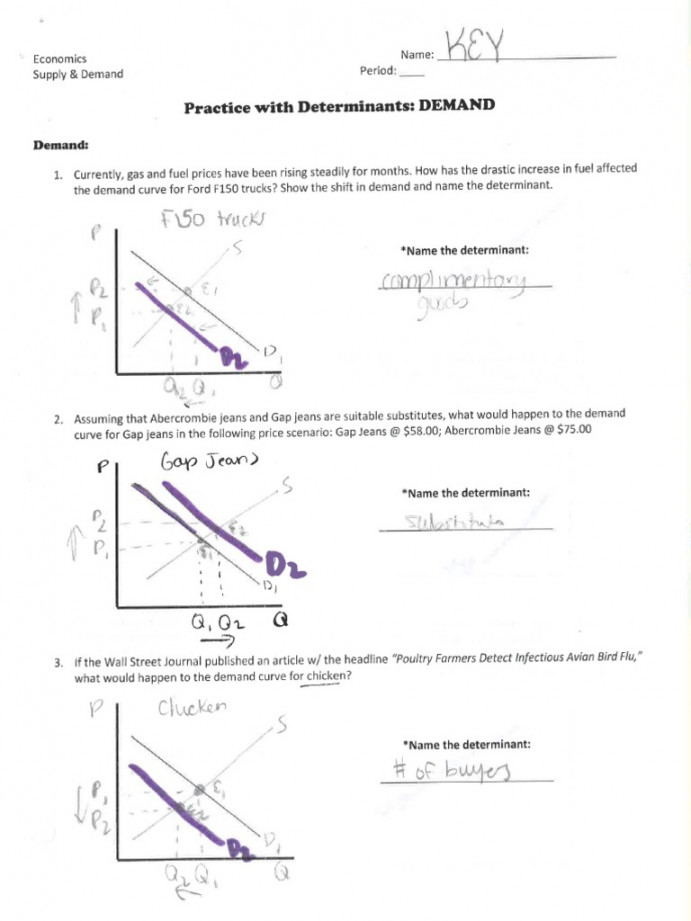
Image: martinlindelof.com
Understanding this fundamental economic principle is crucial for anyone who wants to make informed decisions in today’s dynamic economy. Whether you’re a student grappling with economics concepts or a seasoned professional looking to sharpen your business acumen, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of demand and supply.
What is Supply and Demand?
At its core, supply and demand is the relationship between the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing to offer (supply) and the quantity that consumers are willing to buy (demand) at a given price. When these two forces are in balance, we reach an equilibrium price where the quantity supplied perfectly matches the quantity demanded. But what happens when this balance is disrupted?
Here, the principles of supply and demand become truly captivating. When demand for a product rises, and supply remains constant, the price naturally increases. Think of a sudden surge in demand for winter coats during an unexpected blizzard – the limited supply will lead to higher prices as consumers vie for the scarce warmth. Conversely, when supply increases while demand stays stable, prices tend to fall. Imagine a bumper harvest of oranges leading to a surplus in the market – the abundant supply will drive down the price of oranges.
Key Concepts: A Deep Dive
Demand
Demand refers to the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price, at a specific time. It is not just desire, but the willingness and ability to pay.
Here are the key factors that influence demand:
- Price of the good: The cornerstone of demand. Higher prices typically lead to lower demand, and lower prices encourage higher demand. This is known as the Law of Demand.
- Income: As income rises, consumers tend to demand more, especially of non-essential goods. This is known as a normal good. However, for some goods, demand may fall as income rises. These are known as inferior goods.
- Price of related goods: Substitutes are goods that can be used in place of each other. If the price of a substitute rises, the demand for the original good will increase. Complements are goods that are used together. If the price of a complement rises, the demand for the original good will fall.
- Tastes and Preferences: Consumer preferences and trends play a significant role in demand. For example, a sudden surge in popularity for a particular brand of sneakers can drastically increase its demand.
- Expectations: Consumers’ expectations about future prices and availability can also impact demand. If people expect prices to rise in the future, they may buy more today, leading to a higher demand.
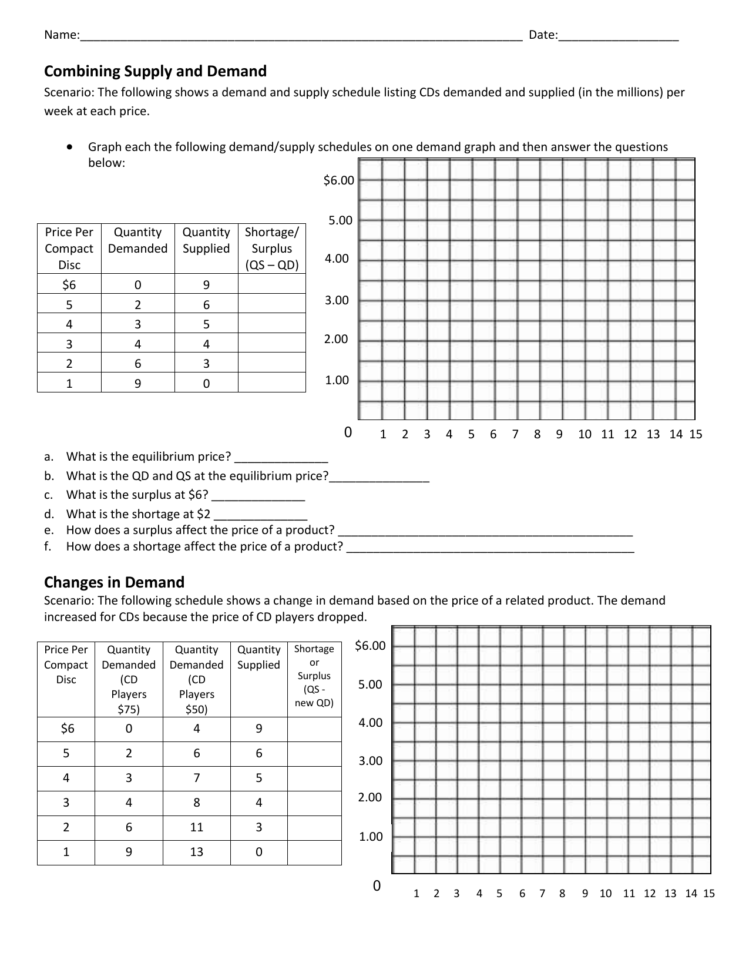
Image: db-excel.com
Supply
Supply refers to the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price, at a specific time. It represents the production capabilities of businesses and the resources they can leverage.
The factors that influence supply are:
- Cost of production: Inputs like labor, raw materials, and energy directly impact the cost of production. Higher production costs usually lead to lower supply. Conversely, lower costs encourage higher supply.
- Technology: Advancements in technology can significantly increase production efficiency and lower costs. This can lead to a higher supply of goods and services.
- Price of related goods: Producers may shift resources toward products with higher prices. If the price of a substitute good rises, the supply of the original good may fall. Likewise, if the price of a complementary good rises, the supply of the original good may increase as producers focus on both products.
- Government policies: Subsidies, taxes, regulations, and trade policies can influence supply. For example, a tax on production would likely reduce supply, while a subsidy would encourage higher supply.
- Number of sellers: A larger number of sellers in the market will generally lead to higher supply. Conversely, fewer sellers will result in a lower supply.
Real-World Applications: From Everyday Decisions to Global Markets
The principles of supply and demand are not confined to theoretical models – they manifest in real-world scenarios every single day, influencing our purchasing decisions, driving business strategies, and shaping the global economy.
Daily Life
Consider your everyday grocery shopping. If the price of bread suddenly skyrockets due to a shortage of wheat, you might look for substitutes like bagels or tortillas. This is an example of how the price of one good influences the demand for another. Or imagine a surge in the demand for reusable water bottles as environmental awareness grows. This increased demand could lead to higher prices for those bottles if suppliers cannot meet the increased demand.
Businesses
Businesses constantly analyze supply and demand to make critical decisions. A clothing retailer might carefully monitor seasonal trends to adjust its inventory, ensuring it has enough stock of sought-after items. Similarly, a tech startup might adjust the price of its new app based on customer feedback and demand trends. Companies that effectively respond to shifts in supply and demand can secure a competitive edge in the market.
Global Markets
The forces of supply and demand influence global trade dynamics. Consider the global oil market. When major oil-producing countries experience political instability, production can be disrupted, leading to a decrease in supply. This, in turn, can drive up oil prices worldwide, affecting everything from gasoline prices at the pump to the cost of air travel.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
Supply and demand are fundamentally intertwined, constantly influencing each other. This dynamic interaction is known as *equilibrium*. Equilibrium is achieved when the price of a good adjusts to the point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. This is the point where both consumers and producers are satisfied, ensuring a stable market.
However, the real-world is rarely in perfect equilibrium. External factors can disrupt this balance. When demand exceeds supply, we experience a shortage, leading to higher prices as consumers compete for scarce goods. Conversely, when supply surpasses demand, we witness a surplus or glut in the market, pushing prices downwards to stimulate consumption.
Practice Makes Perfect: Mastering Demand and Supply
The best way to truly understand supply and demand is through practice. There are numerous online resources, textbooks, and practice exercises readily available. By working through these exercises, you can gain hands-on experience, develop your analytical skills, and build your understanding of this essential economic concept.
Practice exercises can range from basic scenarios to more complex simulations. For instance, you might be asked to analyze the impact of a government tax on the supply of a product or predict the price change of a specific good due to a change in consumer preferences. These exercises not only solidify your knowledge but also provide valuable insights into how the principles of supply and demand play out in real-world contexts.
Demand And Supply Practice Answer Key
Conclusion: A Foundation for Economic Understanding
Supply and demand are the bedrock principles of how markets function. By understanding these forces, you gain a powerful lens to analyze economic trends, make informed business decisions, and navigate the world of commerce with greater clarity. The journey to mastering supply and demand is a continuous process of learning, exploration, and application. So, dive in, practice your skills, and become a master of the market forces that shape our economic landscape.





