Imagine a loved one suddenly struggling to speak, their face drooping, or their arm feeling weak. These are terrifying symptoms that could indicate a stroke, a medical emergency demanding immediate attention. The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), a standardized assessment tool, plays a crucial role in understanding the severity of stroke and guiding treatment decisions. This article will delve into the intricate world of the NIHSS, specifically focusing on Group A answers, offering valuable insights to enhance your understanding of this vital tool.

Image: www.vmesonetwork.com
The NIHSS is a 15-item scale designed to objectively quantify the severity of stroke-related deficits. These items cover various neurological functions, including consciousness, language, vision, motor skills, and coordination. Each item is scored on a scale, typically from 0 to 4, with higher scores indicating more severe neurological impairment. While the scale is comprehensive, Group A stands out as its foundational element, encompassing Level of Consciousness, Eyes, and Motor Function.
Understanding the Framework of Group A: Level of Consciousness, Eyes, and Motor Function
Let’s break down the individual elements of Group A:
1. Level of Consciousness (LOC)
- Score 0: Alert, normal level of consciousness.
- Score 1: Slight drowsiness, but easily aroused.
- Score 2: Drowsy or confused, requires repeated stimulation to maintain wakefulness.
- Score 3: Unresponsive to verbal or painful stimuli.
- Score 4: Unresponsive to any stimuli.
The LOC item assesses the patient’s responsiveness and alertness. Clinicians use verbal commands, light touch, or even painful stimuli to gauge the patient’s response, allowing them to quickly determine the severity of the stroke’s impact on consciousness.
2. Eyes
- Score 0: Eyes open spontaneously.
- Score 1: Eyes open to verbal command.
- Score 2: Eyes open to pain.
- Score 3: No eye opening.
The Eye item evaluates the patient’s ability to open their eyes. This element gives insights into brainstem function, as the brainstem controls essential functions like eye movement.
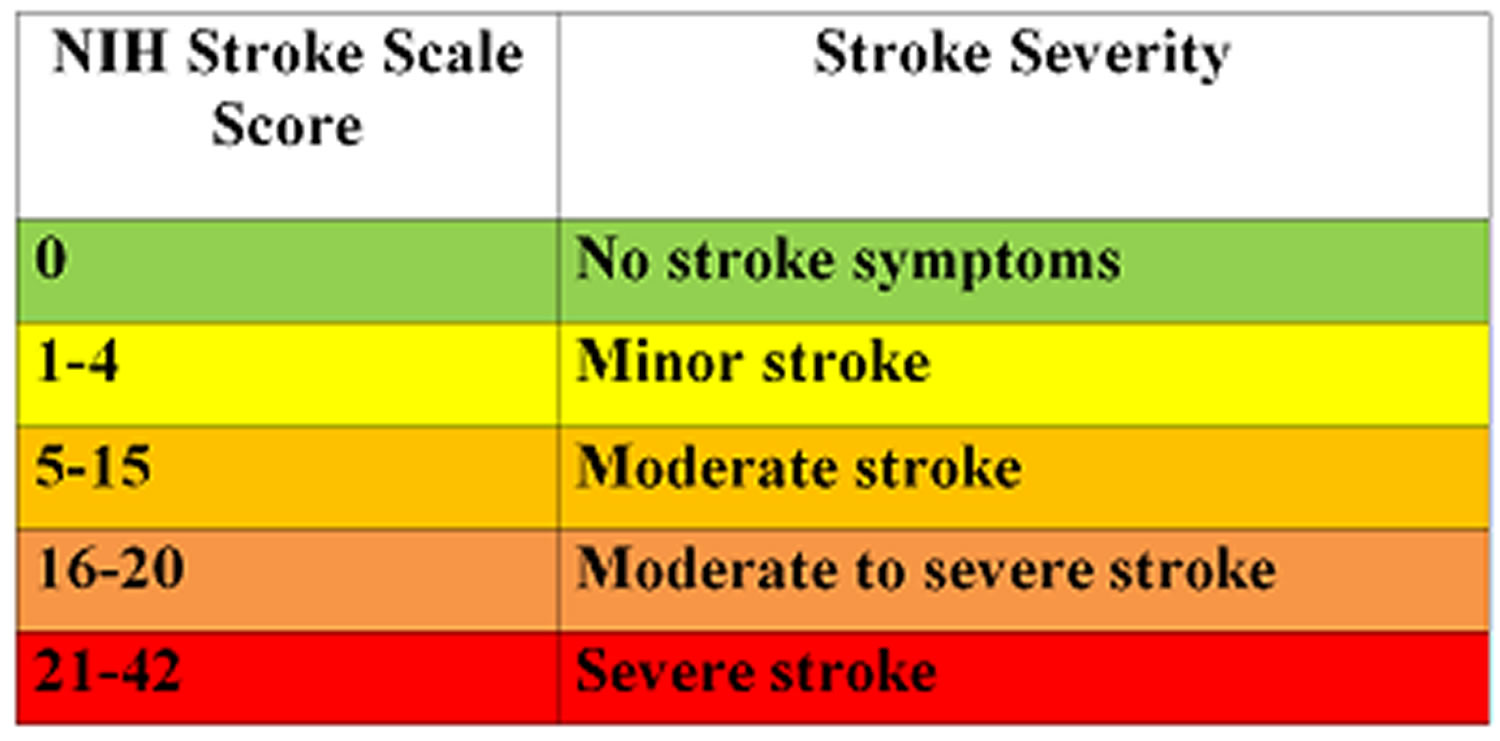
Image: templates.esad.edu.br
3. Motor Function
- Score 0: No drift, normal strength.
- Score 1: Drift, minor weakness.
- Score 2: Some drift, moderate weakness.
- Score 3: Severe drift, significant weakness.
- Score 4: No movement, complete paralysis.
This item assesses upper limb motor function. The patient is asked to extend both arms forward with palms up, and the duration of drift or weakness in the arms is observed. This item helps identify if the stroke has significantly affected the motor cortex controlling voluntary movement.
Importance of Group A:
Group A is pivotal because it provides immediate insight into the severity of the stroke. The patient’s LOC, eye movement, and motor function can be rapidly assessed, allowing medical professionals to prioritize emergency care.
Deciphering Group A: A Step by Step Guide
Let’s illustrate this with a practical example:
Scenario: A 65-year-old patient arrives at the emergency room with sudden onset weakness in the right arm and slurred speech. The doctor proceeds to administer the NIHSS:
- LOC: The patient is alert and responsive to verbal commands, scoring 0.
- Eyes: The patient opens their eyes spontaneously, scoring 0.
- Motor Function (Right Arm): The patient’s right arm drifts downwards when extended forward, scoring 1.
This patient’s score on Group A highlights a moderate level of neurological impairment. The patient is awake and alert but exhibits weakness in one limb, suggesting a possible stroke.
Key Takeaways and Actionable Insights
- The NIHSS is a powerful tool for stroke assessment. It allows for a standardized assessment of stroke severity, facilitating prompt and accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Group A provides a quick assessment of critical neurological functions. Alertness, eye opening, and motor function are assessed, giving immediacy to the severity of the stroke.
- The NIHSS requires training and expertise for accurate interpretation. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to receive proper training to utilize this scale effectively.
- Time is brain. Early identification and treatment are critical in improving neurological outcomes after a stroke. Understanding the NIHSS can allow for faster intervention and potentially minimize long-term damage.
Nihss Stroke Scale Group A Answers
https://youtube.com/watch?v=aVUXf2do70s
Empowering Your Understanding: A Call to Action
The NIHSS is a pivotal tool in the fight against stroke. By understanding its framework, especially the significance of Group A, you can be better prepared to recognize the signs of a stroke and advocate for immediate medical attention. Spread awareness about stroke and its impact, and encourage immediate action should symptoms arise. Remember, every minute counts when it comes to stroke care.





