Have you ever wondered what makes up the world around us? From the tiniest speck of dust to the grandest mountains, everything is composed of atoms. But what exactly are atoms? These tiny building blocks of matter are a fascinating world of subatomic particles, each with its unique properties and roles.

Image: louisvuittonsverige.cc
Understanding the structure of an atom is fundamental to comprehending the world around us. This guide will delve into the core components of an atom, providing insights into their functions and offering valuable assistance in completing a “parts of an atom” worksheet. So, let’s embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm of the atom!
Exploring the Core: The Nucleus
At the heart of every atom lies its nucleus, a dense and positively charged region containing two fundamental particles: protons and neutrons. These tiny building blocks play a crucial role in determining an atom’s identity and stability.
Protons: The Identity Keepers
Protons are positively charged particles with a mass approximately equal to that of a neutron. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, also known as its atomic number, defines the element to which the atom belongs. For example, all carbon atoms contain 6 protons, while all oxygen atoms have 8 protons. This unique identifier ensures that each element has distinct chemical properties and behaviors.
Neutrons: The Stabilizers
Neutrons are electrically neutral particles, meaning they carry no charge. They contribute to the atom’s mass but do not affect its charge. The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can vary, giving rise to different isotopes of the same element. For instance, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, with 6 and 8 neutrons respectively.
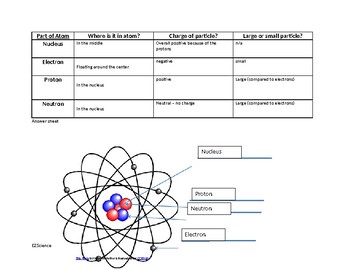
Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
The Electron Cloud: A Realm of Negativity
Surrounding the nucleus is a vast, negatively charged region known as the electron cloud. This region is home to electrons, particles that are incredibly light and carry a negative charge. Electrons are constantly in motion, orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. These shells, which are not actual physical orbits, represent different energy levels that electrons can occupy.
Electron Shells: Energy Levels in the Atom
Each electron shell can accommodate a specific number of electrons. The first shell, closest to the nucleus, can hold up to two electrons. Subsequent shells have higher capacities, with the second shell accommodating up to eight electrons. The arrangement of electrons in these shells influences the atom’s chemical behavior and its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
Worksheet Answer Key: Demystifying the Atom
Now, let’s put our newfound knowledge to the test and decode the answers to a typical “parts of an atom” worksheet. Here’s a breakdown of common questions and their solutions:
1. What are the three main subatomic particles?
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in the electron cloud.
2. What is the atomic number?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It defines the element to which the atom belongs.
3. How do you calculate the mass number?
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. You can calculate it by adding the number of protons and neutrons.
4. What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon, with different numbers of neutrons.
5. What is the role of electrons in chemical bonding?
Electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding. Atoms can share or transfer electrons with other atoms to form stable chemical bonds. The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s outer shell determines its reactivity and ability to form bonds.
Applications in Real-World
The understanding of atomic structure is not merely an academic exercise but a cornerstone of numerous scientific and technological advancements. Here are some practical applications of this knowledge:
- Medicine: Medical imaging techniques like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) rely on the interaction of atomic nuclei with magnetic fields, providing detailed images of internal organs and tissues.
- Energy: Nuclear power plants harness the energy released from the splitting of atoms in a process called nuclear fission, providing a significant energy source.
- Electronics: The development of advanced semiconductor devices, like transistors and integrated circuits, hinges on our understanding of how electrons behave in materials at the atomic level.
- Materials Science: The properties of materials, such as strength, conductivity, and reactivity, are directly related to their atomic composition and structure. These insights drive the creation of new materials with specific functionalities for various applications.
Beyond the Basics: Unveiling the Quantum World
While our journey has provided a solid foundation in the parts of an atom, the story doesn’t end here. The world of the atom is a fascinating realm of quantum mechanics, a branch of physics that governs the behavior of subatomic particles. Quantum mechanics reveals that electrons do not exist in definite orbits but rather as probability clouds, and their energies are quantized, meaning they can only exist at specific discrete levels.
Parts Of An Atom Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion: A Microscopic World of Wonders
From the building blocks of matter to our technological advancements, the understanding of the atom is paramount. By grasping the fundamental concepts of atomic structure, we unlock a deeper comprehension of the world around us. So, keep exploring, keep inquiring, and continue to unravel the secrets hidden within the microscopic realm of the atom!





