Have you ever wondered how your refrigerator keeps your food fresh and cold? Or how air conditioners cool down your home on a sweltering summer day? The magic behind these wonders lies in the fascinating world of refrigeration systems, and two key concepts play a crucial role: superheat and subcooling. These seemingly complex terms are fundamental to understanding how refrigeration cycles operate efficiently and maintain optimal performance.
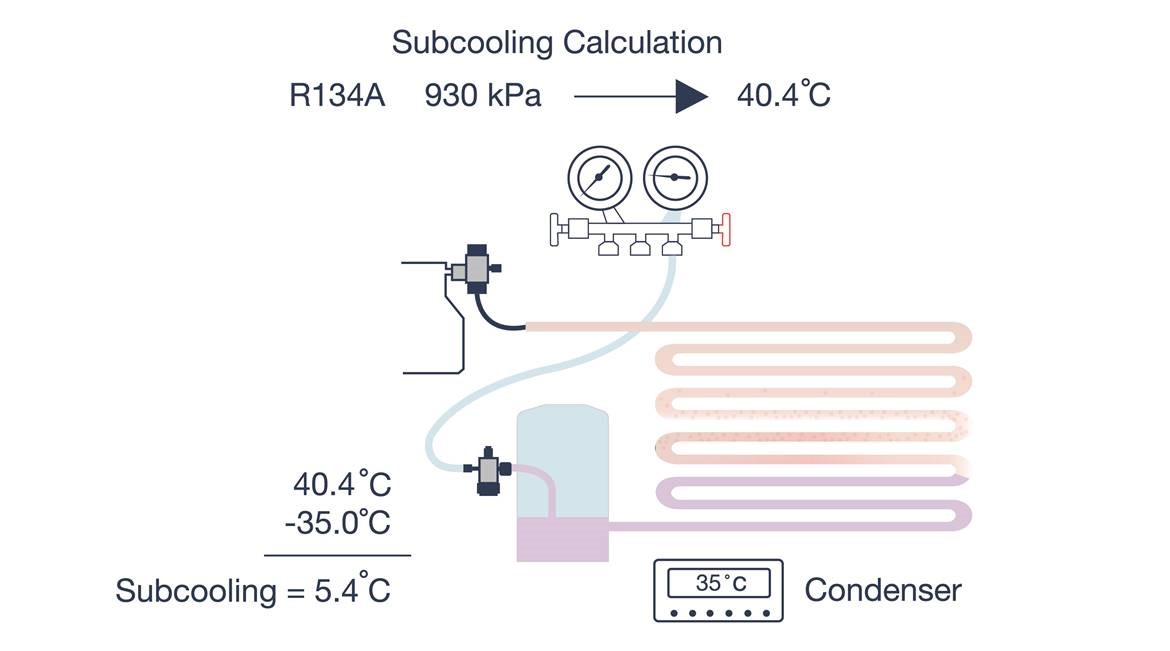
Image: www.technicalpassport.com
In essence, superheat and subcooling are measures of the temperature difference between the refrigerant in a refrigeration system and its corresponding saturation temperature. While they might sound intimidating, they are essential for ensuring the smooth operation of refrigeration systems. By understanding superheat and subcooling, you can troubleshoot common problems, optimize system performance, and even ensure the longevity of your refrigeration appliances.
Understanding Superheat: A Hot Topic in Refrigeration
Superheat refers to the temperature difference between the refrigerant vapor and its saturated vapor temperature at a given pressure. Imagine a pot of water boiling on the stove. The water vapor rising from the pot is saturated vapor— it’s at the point where it’s about to condense back into liquid. Now, if you heat that vapor up further, you’ve created superheat. This added heat ensures the refrigerant is fully vaporized before it enters the compressor, preventing liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor, which could lead to serious damage.
Here’s a simple analogy: Think of a straw inserted into a glass of soda. As you sip, the soda level drops, and the liquid in the straw starts to vaporize, creating a “superheated” bubble.
Why is Superheat Important?
Superheat plays a vital role in the efficient operation of refrigeration systems. Here’s why:
- Preventing Liquid Slugging: Superheat ensures that only vaporized refrigerant enters the compressor. If liquid refrigerant enters, it can lead to a condition called liquid slugging, which damages the compressor.
- Optimizing Compressor Performance: The amount of superheat directly influences compressor efficiency. A proper amount of superheat ensures that the compressor operates smoothly and doesn’t work too hard. Excessive superheat, however, can lead to wasted energy.
- Ensuring Refrigerant Flow: Superheat helps to maintain a consistent flow of refrigerant through the system, ensuring that the desired cooling effect is achieved.
How to Measure Superheat
Measuring superheat involves using specialized tools, such as a digital thermometer or a manifold gauge set. Here’s how it works:
- Measure the Suction Line Temperature: Place the thermometer on the suction line of the refrigeration system. The suction line is the pipe carrying low-pressure refrigerant vapor to the compressor.
- Determine Saturation Temperature: Consult a refrigerant pressure-temperature chart or use a specialized app to find the saturation temperature corresponding to the pressure reading at the suction line.
- Calculate Superheat: Subtract the saturation temperature from the measured suction line temperature. The result is the superheat value, typically measured in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Delving into Subcooling: A Cool Concept
Subcooling, as the name suggests, is the opposite of superheat. It refers to the temperature difference between the refrigerant liquid and its saturated liquid temperature at a given pressure. Imagine cooling down a bottle of soda in the refrigerator. When the soda reaches a certain temperature, it starts to get really cold and might even start forming condensation on the bottle. This is because the soda has reached its saturated liquid temperature. Now, if you continue to cool it down even further, you are subcooling the soda.
Why is Subcooling Important?
Subcooling plays a crucial role in optimizing refrigeration system efficiency and maximizing the cooling capacity. Here’s why:
- Increasing Refrigerant Density: Subcooling increases the density of the refrigerant liquid, allowing the system to hold more refrigerant and, in turn, transfer more cooling energy to the environment.
- Reducing Flash Gas: Subcooling minimizes flash gas, which is the vaporization of refrigerant liquid that occurs when it experiences a pressure drop. This ensures that more refrigerant liquid reaches the evaporator, enhancing cooling capacity.
- Optimizing Condenser Performance: Subcooling helps to ensure that the condenser is working efficiently by maximizing heat rejection, facilitating the transfer of heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding environment.
How to Measure Subcooling
Measuring subcooling requires similar tools as superheat, such as a digital thermometer or a manifold gauge set. Here’s how to do it:
- Measure the Liquid Line Temperature: Place the thermometer on the liquid line, the pipe conveying high-pressure refrigerant liquid to the evaporator.
- Determine Saturation Temperature: Consult a refrigerant pressure-temperature chart or use a relevant app to find the saturation temperature corresponding to the pressure reading at the liquid line.
- Calculate Subcooling: Subtract the measured liquid line temperature from the saturation temperature. The result is the subcooling value, usually expressed in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius.
How Do You Calculate Superheat And Subcooling
Superheat and Subcooling: A Dynamic Duo
Superheat and subcooling are not independent concepts; they are intricately linked and influence each other’s behavior within a refrigeration system. A proper balance between these two parameters is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency.
When the superheat is too high, it can reduce the cooling capacity and increase energy consumption. On the other hand, too much subcooling can lead to reduced refrigerant flow and potential frosting issues in the evaporator. Both superheat and subcooling are crucial variables that should be monitored and adjusted regularly to ensure the proper functioning of your refrigeration system.
In conclusion, understanding superheat and subcooling is fundamental for comprehending the complexities of refrigeration systems. By mastering these concepts, you can optimize system performance, avoid common issues, and prolong the life of your refrigeration appliances. Remember, if you are unsure about how to measure or adjust these values, consult a qualified technician. Happy cooling!





