Imagine a patient, gripped by crushing chest pain, gasping for air, their face pale with fear. This scenario, one that plays out in emergency rooms across the globe, is the stark reality of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). ACS is a life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to the heart is suddenly reduced or blocked, often leading to a heart attack. As nurses, we are on the frontlines, responsible not only for providing immediate care but also for accurately assessing and identifying potential complications. This is where the North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) Nursing Diagnoses come into play, offering a standardized framework that helps us classify and prioritize patient needs.
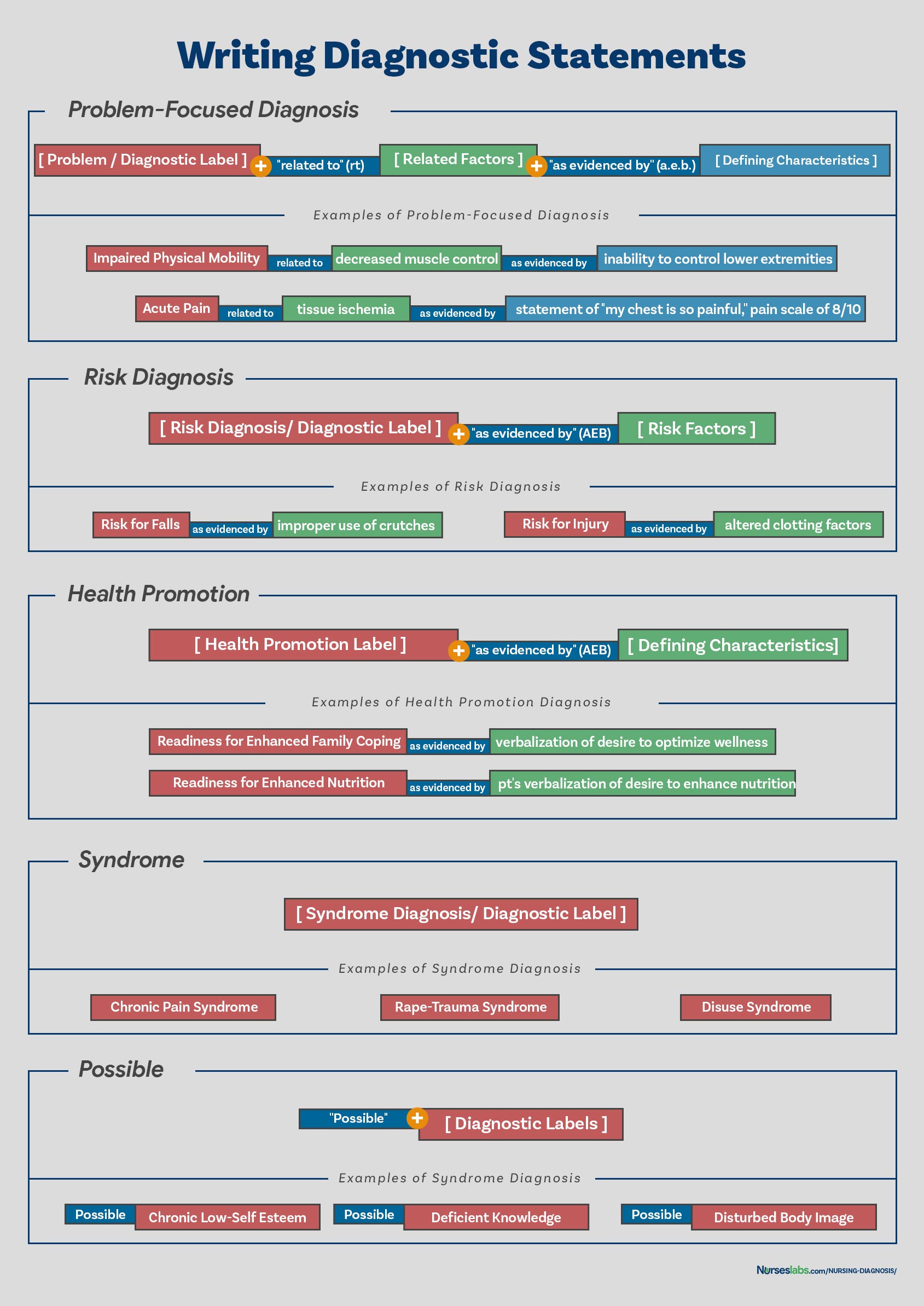
Image: webapi.bu.edu
NANDA diagnoses provide a common language for nurses, promoting consistency in assessment and care planning. In the context of ACS, these diagnoses can highlight specific risks and vulnerabilities faced by patients, enabling us to tailor interventions that optimize outcomes. Understanding NANDA diagnoses for ACS equips nurses with the knowledge to anticipate potential complications, effectively manage symptoms, and advocate for individualized care.
The Importance of NANDA Nursing Diagnoses in ACS
NANDA nursing diagnoses play a crucial role in the care of ACS patients. They allow nurses to identify potential complications, plan interventions, and evaluate the effectiveness of care. By using a standardized language, nurses can communicate more effectively with other healthcare professionals, ensuring that all members of the care team are on the same page.
Common NANDA Nursing Diagnoses for ACS
When caring for patients with ACS, nurses need to assess and recognize various potential complications. NANDA provides a comprehensive framework for identifying these complications and categorizing them into distinct diagnoses. Some of the most common NANDA diagnoses utilized in ACS include:
- Decreased Cardiac Output: This diagnoses is used when the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively is compromised. In ACS, reduced blood flow to the heart can lead to a decline in cardiac output, causing symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion: This diagnosis signifies inadequate blood flow to tissues. In ACS, the reduced oxygen supply to the heart muscle can lead to ischemia, pain, and potentially irreversible damage if not addressed promptly.
- Acute Pain: This diagnosis is frequently encountered in ACS patients who experience chest pain, discomfort, or pressure. The pain can be severe and debilitating, requiring effective pain management strategies.
- Anxiety: The threat of heart attack and the uncertainty surrounding the diagnosis can provoke significant anxiety in ACS patients. It’s important to recognize and address anxiety to promote emotional well-being and facilitate coping mechanisms.
- Fear: Similarly, fear is a common emotion experienced by many individuals facing a heart attack. The potential for death or long-term health consequences can trigger intense fear, necessitating emotional support and reassurance.
- Deficient Knowledge: This diagnosis pertains to the lack of understanding regarding ACS, its causes, and the management strategies involved. Patients need comprehensive education about their condition to actively participate in their care and make informed decisions.
- Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output: This diagnosis is utilized when the patient is at risk of developing decreased cardiac output due to factors like ACS, heart failure, or other cardiovascular conditions.
- Risk for Ineffective Tissue Perfusion: This diagnosis signifies the potential for inadequate blood flow to tissues, which could be associated with factors like ACS, peripheral artery disease, or diabetes.
Understanding the Role of NANDA in Nursing Practice
Let’s delve into why NANDA diagnoses are so crucial for nurses in the management of ACS. Firstly, they provide a standardized framework for communication. Using a common language ensures that all members of the care team are on the same page, promoting clarity and consistency in the delivery of care. Imagine a scenario where one nurse identifies a patient’s need for pain management while another focuses solely on maintaining hemodynamic stability. This lack of communication can result in fragmented care and less than optimal outcomes.
Secondly, NANDA diagnoses facilitate individualized care planning. By identifying specific nursing diagnoses, nurses can tailor their interventions to meet the unique needs of the individual patient. A patient with severe chest pain may require more frequent assessments and more aggressive pain management strategies compared to a patient who is experiencing milder discomfort. Finally, NANDA diagnoses serve as a valuable tool for documenting progress and evaluating outcomes. By recording the nursing diagnoses, interventions, and patient responses, nurses can monitor the effectiveness of care and make necessary adjustments as needed. This allows for continuous improvement in patient care and a better understanding of what interventions are most effective in managing specific complications.

Image: nickmeowhenson.blogspot.com
Tips for Applying NANDA Diagnoses in ACS
As nurses caring for patients with ACS, here are some key tips to enhance your understanding and application of NANDA diagnoses:
- Thorough Assessment: The first step in applying NANDA diagnoses is a comprehensive assessment. Gather information from the patient, review their medical history, and perform a physical exam. Assess vital signs, pain levels, and any other relevant symptoms.
- Collaborate with Colleagues: Consult with other nurses, doctors, and specialists involved in the patient’s care. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and help you formulate an accurate nursing diagnosis.
- Critical Thinking: Apply critical thinking skills to analyze the data you’ve gathered. Consider the patient’s history, current situation, and potential complications. This will help you choose the most relevant and accurate NANDA diagnoses.
- Documentation: Clearly document the chosen nursing diagnoses in the patient’s medical record. Include the rationale for your decisions and how these diagnoses relate to the patient’s overall care plan.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly reassess the patient’s condition to determine the effectiveness of interventions and identify any changes in their needs. Adjust nursing diagnoses and interventions accordingly.
The Impact of NANDA on Patient Outcomes
The use of NANDA nursing diagnoses has been shown to have a positive impact on patient outcomes in various clinical settings, including ACS. By identifying and addressing specific patient needs, nurses can optimize care, improve symptom management, and reduce complications. For instance, recognizing the NANDA diagnosis Anxiety in an ACS patient might encourage nurses to implement strategies like relaxation techniques, providing emotional support, and informing the patient about their condition.
By understanding the underlying rationale behind these diagnoses, nurses can better anticipate the needs of their patients and tailor their interventions to improve overall outcomes.
FAQ
What are the key differences between NANDA nursing diagnoses related to ACS?
NANDA diagnoses for ACS focus on specific complications of the condition. For example, Decreased Cardiac Output pertains to the heart’s pumping ability, while Ineffective Tissue Perfusion focuses on blood flow to tissues. Understanding these distinctions helps nurses tailor interventions to address these specific issues.
How can nurses use NANDA diagnoses to improve communication with other healthcare professionals?
NANDA provides a standardized language that facilitates communication between nurses and other healthcare professionals like doctors and pharmacists. Using NANDA diagnoses ensures everyone understands the patient’s needs and care plan. For example, a nurse can communicate with a physician about the patient’s Acute Pain diagnosis, prompting the doctor to prescribe appropriate pain medication.
What are some resources available for nurses to learn more about NANDA diagnoses?
NANDA International (NANDA-I) is the official organization that develops and maintains NANDA diagnoses. Their website provides extensive information on various diagnoses, including those relevant to ACS. Additionally, numerous textbooks and online resources offer detailed explanations and examples of NANDA diagnoses in various clinical settings.
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis For Acute Coronary Syndrome
Conclusion
NANDA nursing diagnoses are invaluable tools for nurses caring for patients with ACS. By promoting a standardized framework for communication, facilitating individualized care planning, and documenting progress, NANDA diagnoses help us provide safe and effective care that prioritizes the unique needs of each patient. By embracing NANDA diagnoses in your practice, you can enhance your understanding of ACS, improve patient outcomes, and further develop your nursing expertise.
Are you interested in learning more about specific NANDA diagnoses relevant to ACS? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.





