It all started in high school chemistry class. We were learning about the different shapes of molecules, and I was completely lost. How could water be bent, and methane a perfect tetrahedron? It seemed like magic. Then, my teacher introduced us to VSEPR theory, and everything clicked. It turns out the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, its *molecular geometry*, can be predicted based on simple rules. I suddenly felt empowered, capable of understanding the intricate world of molecular shapes. This journey of understanding molecular geometry led me to discover the invaluable resource of a **molecular geometry worksheet with answers PDF**. It was a game-changer, not only for me but countless others too.
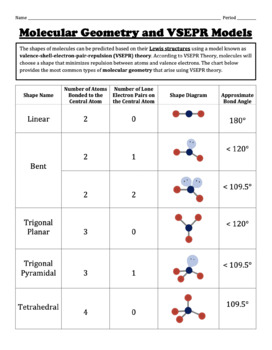
Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
If you’re struggling to wrap your head around the shapes of molecules, don’t fret! You’re not alone. Molecular geometry is a crucial concept in chemistry, and understanding it unlocks a deeper comprehension of how molecules behave. This article will guide you through the world of molecular geometry and provide you with the ultimate resource – a **molecular geometry worksheet with answers PDF** – to help you master this concept.
Understanding Molecular Geometry: The Building Blocks of Chemistry
Molecular geometry describes the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It’s not just about aesthetics; it’s about functionality. The shape of a molecule influences its properties, such as its reactivity, polarity, and even how it interacts with other molecules. This is because the arrangement of atoms determines the distribution of electron density and the location of functional groups within the molecule. These factors, in turn, influence the molecule’s interactions with other molecules and even how it interacts with light.
To understand molecular geometry, we need to delve into the world of electron pairs. Every atom in a molecule has a certain number of valence electrons, which are the electrons involved in bonding. These valence electrons exist in pairs, forming bonding and nonbonding pairs. It’s the repulsion between these electron pairs, both bonding and nonbonding, that dictates the geometry of a molecule.
VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometry
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a powerful tool used to predict molecular geometry. VSEPR theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize the repulsion between them. This leads to various predictable geometries, with the number of electron pairs determining the shape of the molecule.
Key Concepts of VSEPR Theory:
- Electron Pairs: Both bonding and nonbonding electron pairs around a central atom contribute to repulsion.
- Lone Pairs: Nonbonding electron pairs (lone pairs) exert stronger repulsion than bonding pairs.
- Hybridization: The concept of hybridization helps explain the formation of the electron pairs, with orbitals combining to form hybrid orbitals for bonding.

Image: imagekelly8.blogspot.com
Exploring the Common Molecular Geometries
By applying VSEPR theory, we can predict the following common molecular geometries:
Linear Geometry:
In linear geometry, the central atom is bonded to two other atoms, with a bond angle of 180 degrees. Examples include carbon dioxide (CO2) and beryllium chloride (BeCl2).
Trigonal Planar Geometry:
In trigonal planar geometry, the central atom is bonded to three other atoms, with bond angles of 120 degrees. Examples include boron trifluoride (BF3) and formaldehyde (CH2O).
Tetrahedral Geometry:
In tetrahedral geometry, the central atom is bonded to four other atoms, with bond angles of 109.5 degrees. Examples include methane (CH4) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
Trigonal Pyramidal Geometry:
In trigonal pyramidal geometry, the central atom is bonded to three other atoms and has one lone pair, with bond angles of approximately 107 degrees. An example is ammonia (NH3).
Bent or Angular Geometry:
In bent geometry, the central atom is bonded to two other atoms and has two lone pairs, with a bond angle of less than 109.5 degrees. An example is water (H2O).
The Importance of Practice: Molecular Geometry Worksheets with Answers
Understanding molecular geometry is essential for success in chemistry. To solidify your grasp of this concept, there’s no better way than to practice with **molecular geometry worksheets with answers PDF**. These invaluable resources provide a structured framework for learning, allowing you to apply VSEPR theory through solving problems and comparing your answers to the provided solutions.
Tips and Expert Advice for Mastering Molecular Geometry:
- Visualize the Molecules: Use molecular modeling kits or online tools to build 3-D models of molecules and understand their geometry more readily.
- Study the Examples: Explore the molecular geometries of common molecules like methane, water, ammonia, and carbon dioxide to gain a strong foundation.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Regularly work through molecular geometry worksheets, focusing on understanding the connection between the Lewis structure, the number of electron pairs, and the resulting molecular geometry.
By following this advice and utilizing **molecular geometry worksheets with answers PDF**, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of this essential chemical concept and be well-equipped to tackle more complex topics in chemistry.
Frequently Asked Questions about Molecular Geometry:
Q: What are the different types of molecular geometries?
A: The most common molecular geometries include linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, and bent. A molecule’s shape is determined by the arrangement of atoms and electron pairs around the central atom.
Q: How can I determine a molecule’s geometry?
A: The VSEPR theory provides a reliable method for predicting molecular geometry. You can also use Lewis structures to represent the bonding and nonbonding electron pairs around the central atom.
Q: What are the applications of molecular geometry in real life?
A: Molecular geometry plays a crucial role in numerous fields, including:
- Drug Design: Understanding molecular geometry is essential for designing drugs that bind specifically to target receptors in the body.
- Materials Science: The shape of molecules determines the properties of materials, such as their strength, conductivity, and optical properties.
- Environmental Chemistry: The geometry of pollutants impacts how they interact with the environment and how effectively they can be mitigated.
- Biochemistry: The shape of biomolecules, like proteins and enzymes, dictates their function and interactions in living organisms.
Molecular Geometry Worksheet With Answers Pdf
Conclusion
Mastering molecular geometry is a fundamental step in unlocking the secrets of chemistry. By using **molecular geometry worksheets with answers PDF** and applying VSEPR theory, you can decipher the shapes of molecules and understand how these shapes influence their properties and interactions. Embrace the challenge of learning molecular geometry, and you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of chemistry!
Are you interested in learning more about molecular geometry? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!





