Remember those frustrating moments in high school geometry class, struggling with angles, lines, and shapes? I certainly do. I vividly recall staring at a complex diagram, feeling completely lost amidst a sea of theorems and postulates. The answer key, that elusive treasure trove of solutions, seemed so distant and unattainable. But what if I told you that understanding geometry basics could be an enriching and empowering experience?
Image: gustavogargiulo.com
This article is your comprehensive guide to mastering Unit 1 geometry basics. We’ll unpack the fundamentals, explore practical applications, and even debunk some common misconceptions. Prepare to embark on a journey that transforms your understanding of this fascinating subject!
Unlocking the Foundations of Geometry
Geometry, at its core, is the study of shapes, sizes, and the relationships between objects in space. It’s a foundational subject with practical applications in diverse fields – from architecture and engineering to art and design. Unit 1 typically focuses on the building blocks of geometry, introducing concepts that form the basis for more advanced topics.
These fundamental building blocks include:
1. Points, Lines, and Planes
Geometry begins with the most basic elements: points, lines, and planes. A point is an exact location in space, represented by a dot. A line is a collection of infinitely many points that extend infinitely in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions.
2. Angles and Their Types
Angles are formed by two rays that share a common endpoint called the vertex. Angles are classified based on their measures: acute, right, obtuse, straight, and reflex angles. Understanding angle relationships, such as complementary and supplementary angles, is crucial for solving geometric problems.
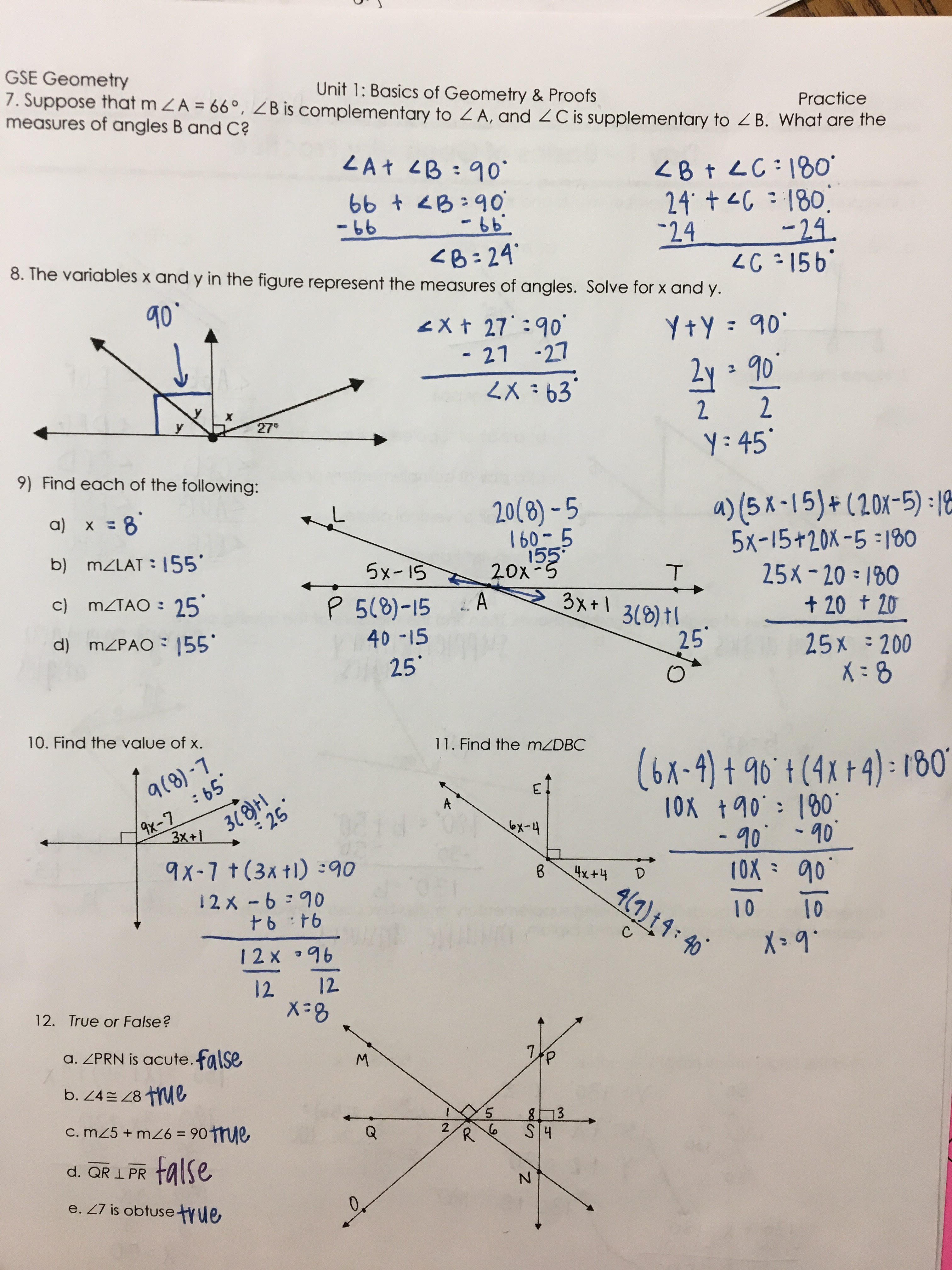
Image: classzonebarth.z13.web.core.windows.net
3. Polygons and Their Properties
Polygons are closed figures formed by straight line segments. Different types of polygons, including triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons, are characterized by their number of sides and angles. Key properties like the sum of interior angles and the relationship between sides and angles are essential to understanding polygons.
4. Geometric Constructions
Geometric constructions involve creating figures using only a compass and a straightedge. Learning to perform basic constructions, such as constructing a perpendicular bisector or an angle bisector, helps develop geometric intuition and problem-solving skills.
5. Area and Perimeter
Area refers to the amount of space a two-dimensional figure occupies, while perimeter is the total distance around the figure. Formulas for calculating area and perimeter for various polygons are fundamental concepts in geometry.
Mastering Geometry Basics: Practical Tips
Here are some tips to help you grasp Unit 1 geometry basics:
1. Visualize and Draw
Geometry is a visual subject. Always visualize shapes and draw diagrams to help you understand the concepts. Drawing your own diagrams can lead to better understanding and problem-solving.
2. Practice, Practice, Practice
Like any skill, geometry requires practice. Work through numerous problems and examples to solidify your understanding of the concepts. Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you get stuck!
3. Connect Concepts
Look for connections between different concepts in geometry. Building on prior knowledge and understanding how ideas relate to one another will make learning more effective.
4. Don’t Memorize, Understand
Instead of memorizing formulas and theorems, strive to understand their underlying logic and reasoning. This will help you apply them confidently in a variety of contexts.
FAQs About Unit 1 Geometry Basics
Q: What is the difference between a line and a line segment?
A: A line extends infinitely in both directions, while a line segment has two endpoints.
Q: Why is it important to know the properties of different polygons?
A: Understanding polygon properties helps solve problems involving area, perimeter, and angles within those figures. It also lays the foundation for more advanced geometric concepts.
Q: How can I practice geometric constructions without a compass and straightedge?
A: There are many online tools and virtual manipulatives that allow you to practice geometric constructions digitally.
Q: What are some real-world applications of geometry?
A: Geometry is applied in countless fields, including architecture, engineering, design, surveying, astronomy, and computer graphics.
Unit 1 Geometry Basics Answer Key
https://youtube.com/watch?v=aVTBvgN2850
Conquering Geometry Basics – A Call to Action
Mastering Unit 1 geometry basics lays the foundation for understanding more complex geometric concepts. It opens doors to various fields and equips you with critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Remember, visualizing, practicing, connecting, and understanding are key to success. Are you ready to unlock the wonders of geometry and take your learning to new heights?





