Have you ever encountered a malfunctioning electrical component in your trusty 2004 Dodge Dakota? Perhaps the headlights flickered, the power windows refused to cooperate, or the radio suddenly went silent. While these issues can be frustrating, they are often relatively easy to troubleshoot with the help of the Dakota’s fuse box diagram. This essential document acts as a road map, guiding you through the intricate labyrinth of your vehicle’s electrical system.
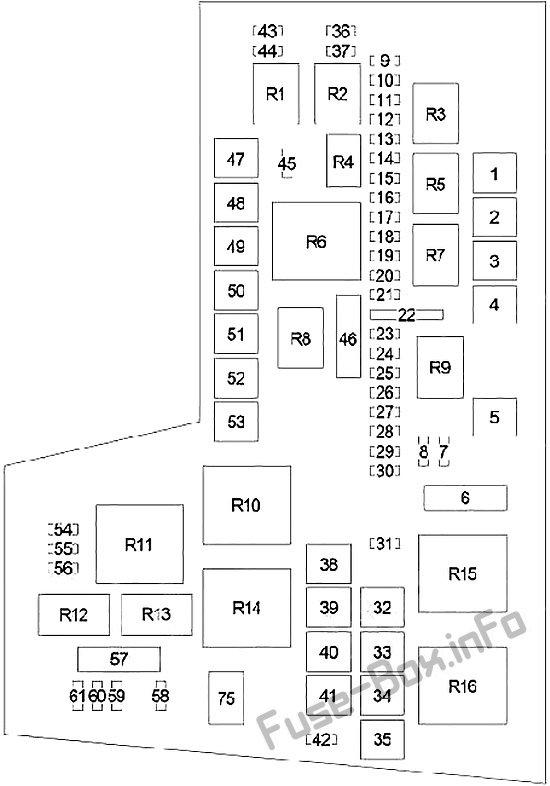
Image: circuitengineschmid.z21.web.core.windows.net
Understanding the 2004 Dodge Dakota fuse box diagram is a crucial skill for any Dakota owner. It equips you with the knowledge to identify and replace blown fuses, diagnose electrical problems, and even perform minor repairs without the need for expensive professional assistance. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the Dakota’s fuse box diagram, explaining its purpose, layout, and how to use it effectively to keep your truck running smoothly.
The Role of the Fuse Box in Your Dakota’s Electrical Symphony
Imagine the electrical system of your 2004 Dodge Dakota as a complex orchestra. Each electrical component, from the headlights to the radio, is like a musician, playing its part in the harmonious functionality of the vehicle. The fuse box acts as the conductor, ensuring that each musician receives the appropriate amount of electrical current to function properly. Fuses, those small, cylindrical devices, are the musical notes – they protect the electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits.
Each fuse within the box is specifically designed to handle a certain amount of current. When an overload or short circuit occurs, the fuse melts, breaking the electrical circuit and preventing further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. This “sacrifice” protects other components from potentially catastrophic failures.
Location, Location, Location: Finding Your Dakota’s Fuse Box
The 2004 Dodge Dakota boasts two fuse boxes, each strategically placed to easily access the components they protect.
- Under the Hood: This fuse box, often called the engine compartment fuse box, is located in the engine bay, readily accessible by lifting the hood.
- Inside the Cabin: The passenger compartment fuse box, also known as the interior fuse box, is typically located on the driver’s side of the dashboard, near the steering wheel.
Deciphering the Language: Reading Your Dakota’s Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is a visual map of your Dakota’s electrical system, providing detailed information about the location of each fuse and the components it protects. Each diagram is a masterpiece of technical art, packed with information that can be daunting at first glance. But fear not, with a little patience and guidance, you’ll learn to decipher this electrical code.
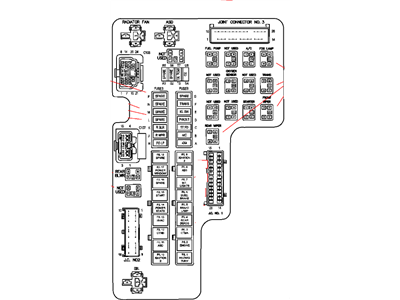
Image: www.moparpartsgiant.com
Key Elements of the Fuse Box Diagram:
- Fuse Locations: The diagram clearly indicates the position of each fuse within the box, often represented by numbered circles or squares.
- Fuse Ratings: Each fuse is assigned a numerical value, representing its maximum amperage (A) capacity. This rating is crucial for ensuring that you replace blown fuses with the correct type, matching the original rating.
- Component Labels: The diagram clearly labels the electrical components protected by each fuse. Common components include headlights, taillights, power windows, radio, and various accessories.
- Color Codes: Some diagrams utilize color codes to distinguish fuse types, such as low-amperage fuses from high-amperage fuses.
Practical Applications: Using the Fuse Box Diagram
Troubleshooting a Malfunctioning Electrical Component:
Let’s say your Dakota’s headlights are malfunctioning. This is a common problem that can be addressed with a little electrical detective work.
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the section of the fuse box diagram dedicated to headlights. You’ll typically find a dedicated fuse for each headlight assembly.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully examine the fuse corresponding to the affected headlight. Look for signs of a blown fuse, such as a broken filament or a melted metal strip.
- Replace the Fuse: If you find a blown fuse, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never replace a blown fuse with a higher amperage fuse, as this can lead to electrical damage and fires.
- Test the System: After replacing the fuse, turn on the headlights to test if the problem has been resolved.
Other Applications:
The fuse box diagram can be used for a wide range of other tasks, including:
- Identifying Fuse Types: You can use the diagram to determine the type of fuse needed for each electrical circuit. This is essential when you need to replace a fuse that has blown.
- Locating Specific Components: The diagram can help you identify the fuse responsible for powering a particular component, allowing you to troubleshoot electrical problems more effectively.
- Planning Electrical Modifications: If you’re planning on adding new electrical components to your Dakota, the fuse box diagram can help you determine the appropriate fuse and circuit to connect them to.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Fuse Box Tips
While the fuse box diagram is a powerful tool, there are several advanced tips that can elevate your electrical troubleshooting skills to the next level:
- Carry a Spare Set of Fuses: Having a spare set of fuses on hand can save you time and hassle when a fuse blows, especially if you’re stranded on the road.
- Familiarize Yourself with Common Fuses: Understanding the common types of fuses, such as blade fuses, ATO fuses, and mini fuses, can make your life easier when purchasing replacement fuses.
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter is a valuable tool for more advanced diagnostics. It allows you to measure voltage, current, and resistance, which can help you pinpoint electrical problems more accurately.
- Safety First: Always disconnect the battery before working on the fuse box to avoid electrical shocks. Additionally, be careful not to touch the metal contacts of the fuses, as they can carry a live charge even if the fuse has blown.
2004 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Diagram
Conclusion: Master Your Dakota’s Electrical Symphony
Understanding your 2004 Dodge Dakota’s fuse box diagram can transform your relationship with your truck. With this knowledge, you can confidently troubleshoot minor electrical problems, saving yourself time, money, and frustration. It’s like gaining a backstage pass to your Dakota’s electrical system, allowing you to understand its intricacies and keep it performing at its best. So, take some time to study your fuse box diagram and become the maestro of your Dakota’s electrical symphony. Remember, a well-maintained electrical system is essential for a safe and enjoyable driving experience.





