Imagine the heartbreak and fear of a woman struggling with an ectopic pregnancy. This life-threatening condition, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, demands immediate medical attention and delicate care. As nurses play a critical role in supporting these patients, understanding a comprehensive nursing care plan for ectopic pregnancy becomes crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of this medical journey, providing a roadmap for nurses to offer compassionate and expert care to women facing this challenge.

Image: www.studypool.com
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This can lead to severe complications, including rupture of the fallopian tube, internal bleeding, and even death. Navigating this complex medical landscape requires a team of dedicated healthcare professionals, and nurses play a vital role in ensuring the safety and well-being of the patient.
Understanding the Nature of Ectopic Pregnancy
Before we delve into the intricacies of a nursing care plan, let’s grasp the underlying principles of this medical condition. Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants somewhere outside the uterine cavity. This most commonly happens in the fallopian tubes, but it can occur in other locations like the ovary, the cervix, or even the abdomen. While the exact cause of ectopic pregnancy remains unknown, several factors can increase the risk, including:
-
Previous history of ectopic pregnancy: Unfortunately, women who have experienced ectopic pregnancy before are at a higher risk of experiencing it again.
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): Infections within the reproductive system can scar the fallopian tubes, making it difficult for the fertilized egg to travel to the uterus.
-
Endometriosis: This condition involves the growth of uterine-like tissue outside the uterus, potentially interfering with the egg’s journey.
-
Tubal ligation or tubal surgery: Previous surgeries involving the fallopian tubes can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
-
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART): Procedures like in vitro fertilization (IVF) can also contribute to a slightly higher risk.
-
Smoking: Nicotine can negatively affect the fallopian tubes’ cilia, tiny hair-like structures that help propel the egg toward the uterus.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is paramount in managing ectopic pregnancy effectively. Identifying the condition promptly can significantly improve the chances of a positive outcome. The key symptoms to look out for include:
-
Abdominal pain: This can range from mild cramping to excruciating pain, often localized on one side of the abdomen.
-
Vaginal bleeding: This may be light spotting or heavier bleeding, often accompanied by pain.
-
Missed menstrual period: While not exclusive to ectopic pregnancy, a missed period, especially when combined with other symptoms, should raise concern.
-
Shoulder pain: This peculiar symptom arises from internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm, causing referred pain to the shoulder.
-
Faintness or dizziness: This could indicate internal bleeding resulting in low blood pressure.
If a woman presents with any of these symptoms, particularly when accompanied by abdominal pain, immediate medical attention is vital. Prompt diagnosis and subsequent intervention can make a significant difference in the patient’s health outcomes.
Navigating the Diagnosis: A Multifaceted Approach
A comprehensive assessment involving a combination of medical history, physical examination, and various tests are crucial for confirming the diagnosis. Here’s how nurses can play a vital role:
-
Taking a Detailed History: A thorough history encompassing menstrual history, past medical conditions, and potential risk factors like previous surgeries or sexually transmitted infections is essential.
-
Physical Examination: A careful physical examination, including the abdomen and pelvic area, helps assess tenderness, signs of bleeding, and any other relevant observations.
-
Confirmation through Imaging: Ultrasound imaging plays a critical role in confirming the diagnosis. Transvaginal ultrasound, which allows a closer look at the pelvic organs, can often visualize the ectopic pregnancy.
-
Lab Tests: Blood tests are crucial for assessing hCG levels, a hormone produced during pregnancy. A slower-than-expected rise in hCG levels or even a decrease can be indicative of ectopic pregnancy.
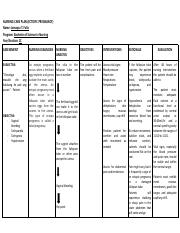
Image: www.coursehero.com
The Nursing Care Plan: Providing Comprehensive Support
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the nursing care plan for ectopic pregnancy begins. This plan is tailored to the individual patient, taking into account her specific situation and medical needs. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
1. Pain Management
-
Analgesics: Administer pain medications, such as opioids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to manage pain effectively.
-
Non-Pharmacological Pain Relief: Encourage relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or guided imagery, to supplement pain management.
2. Monitoring Vital Signs
-
Regular Vital Checks: Closely monitor vital signs, including blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and respiratory rate, to assess for signs of shock or internal bleeding.
-
Hemodynamic Monitoring: In cases of suspected internal bleeding, advanced hemodynamic monitoring may be necessary to track blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital parameters.
3. Emotional Support
-
Empathy and Compassion: Acknowledge the emotional distress associated with an ectopic pregnancy. Provide a safe and empathetic environment for the patient to express her feelings.
-
Information and Education: Explain the diagnosis and treatment options clearly and compassionately. Address any concerns and answer questions patiently.
-
Support Groups and Resources: Refer the patient to support groups or online resources available for women facing ectopic pregnancy.
4. Medication Administration
-
Methotrexate: For early ectopic pregnancies, methotrexate, a medication that terminates the pregnancy, might be administered. Accurate dosage and administration are critical for this treatment.
-
Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection, especially in cases where surgery is performed.
5. Surgical Intervention
-
Salpingostomy: If the ectopic pregnancy is found early and does not have ruptured the fallopian tube, a surgery called salpingostomy can be performed to remove the pregnancy tissue.
-
Salpingectomy: If the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured the fallopian tube, a salpingectomy, which is the removal of the fallopian tube, may be necessary.
-
Laparoscopic surgery: This minimally invasive procedure is often preferred, allowing smaller incisions and quicker recovery times.
-
Emergency Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe internal bleeding, emergency surgery might be required to stop the bleeding and stabilize the patient.
6. Post-Surgical Care
-
Monitoring Recovery: After surgery, closely monitor vital signs, incision sites, and pain levels. Address any concerns related to incision care, wound healing, and pain management.
-
Psychosocial Support: Provide ongoing emotional support and guidance as the patient processes the experience and navigates the emotional and physical challenges.
-
Follow-up Care: Emphasize the importance of scheduled follow-up appointments with her healthcare provider to assess her recovery and discuss future pregnancy plans.
7. Providing Hope and Guidance
-
Future Pregnancy Plans: Help the patient explore options for future pregnancies, including adoption, IVF, or natural conception, if desired.
-
Counseling and Support Resources: Refer her to specialists who can provide counseling and support for coping with the emotional and psychological impact of an ectopic pregnancy.
Expert Insights: Empowering the Nursing Team
Here are some valuable insights from experienced nurses who specialize in caring for women with ectopic pregnancy:
-
“The emotional toll on patients can be immense. It’s vital to create a compassionate and supportive environment where they feel heard and understood.” This emphasis on emotional support underscores the importance of empathic care.
-
“Early detection is key. Encourage women to report any unusual symptoms and seek immediate medical attention.” This highlights the need for prompt action and early intervention.
-
“Remember, each patient is unique. Customize the care plan to address their specific needs and concerns.” This underscores the importance of individualized care and tailored approaches.
Empowering Patients: Taking Control of Their Health
Beyond medical care, empower patients to actively participate in their journey toward recovery by:
-
Educating them about the condition: Provide clear and concise information about ectopic pregnancy, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
-
Encouraging open communication: Foster an environment where patients feel comfortable asking questions and voicing their concerns.
-
Supporting healthy lifestyle choices: Encourage patients to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, to promote overall health and well-being.
Nursing Care Plan For Ectopic Pregnancy
A Final Message of Hope and Resilience
An ectopic pregnancy is a complex and emotionally challenging experience. However, with the right support, medical interventions, and emotional guidance, these women can navigate this difficult journey. Nurses, as compassionate caregivers, play a crucial role in providing comprehensive support and ensure the safety and well-being of their patients. Remember, by fostering empathy, understanding, and a commitment to excellence, we empower women facing ectopic pregnancy to regain their health and embrace a brighter future.
If you or someone you know is experiencing the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, seek immediate medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can improve your chance of a positive outcome and ensure a healthier future.





